- Each bit of memory is an array of bytes
- Each byte is 8 bits
- An integer is 4 bytes. That should give some context!
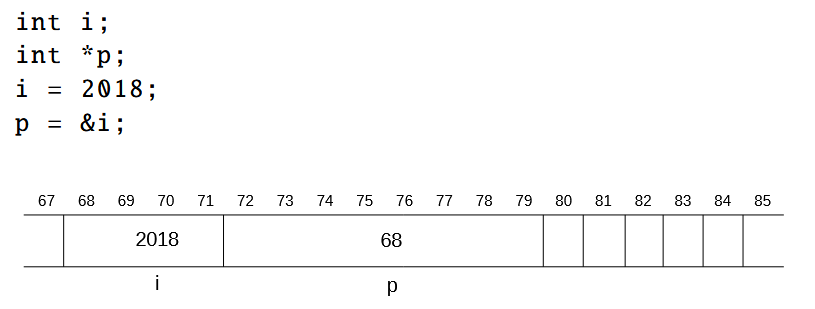
- The
itakes up 4 bytes and pointers take up8bytes. Pointers point to the first address in the bigger “array” that a whole variable occupies
Automatic sizeof when adding
Doing this:
int a[2]
int* p = a + 2The “2” is actually 2 * sizeof(int) which C does automatically cuz it knows the array type
Memory regions:
- Text
- Stores “code” (function pointers point here!)
- Global
- Stores global variables
- Stack
- Stores function calls + local variables + return addresses
- Heap
- Where manual (de)allocation is done. For data that will task outside of functions