union test {
int a; int b[4]; long c;
// This union is sizeof(int) * 4 large
// since that is the biggest field
}- A type that stores 1 of several types (but are mutually exclusive)
- It can only store 1 type at a time
- I.e. “I want an array where everything is either an int or double”. Unions come into play there
Unlike a struct, all the variables share 1 unit of memory (the largest of the given). You can edit any of the vars like a struct tho, but depending on the value it might edit less that all of the memory cells available (i.e. updating int when u have a int and long long)
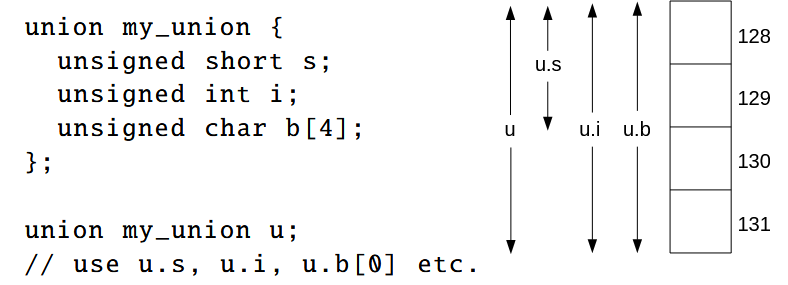
union a_union {
unsigned short s; unsigned int i; unsigned char b[4];
};
int main() {
union a_union test;
test.i = 0b11111111111111111111111111111111; test.s = 0;
printf("%u\n", test.i); // 4294901760 (4294967295 - 65535)
printf("%u\n", test.s); // 0
}Union / Enum idiom
- Unions aren’t that safe: U need to remember what case a union var is in o_O
- Use a struct that matches a
tag(enum) with a union fordatato do that!
struct int_or_double {
enum { INT , DOUBLE } tag;
union {
int i;
double d;
} data;
};