A “bank” of n flip-flops that share a common clock
- Basically the go-to way to store a multi-bit value
- Each flip flop stores 1 bit; registers allow you to store more than 1 bit (like 32 bits)
- An n-bit register has n flip flops
- ”collection of flip flops”
There are two kinds: Load and Shift registers
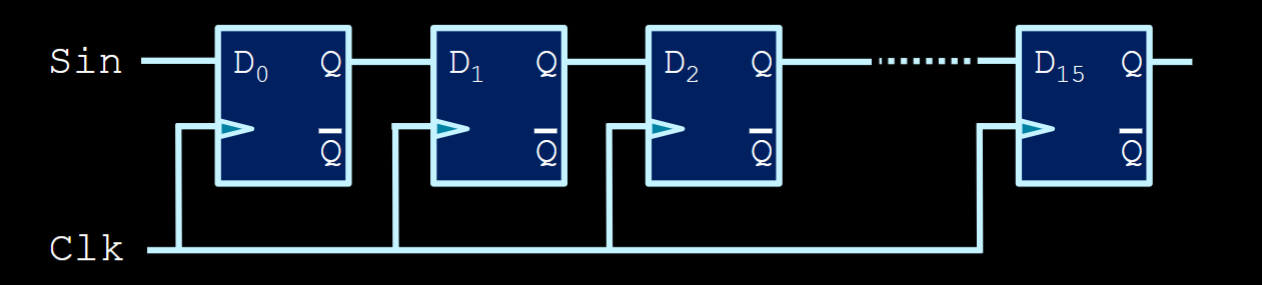
Shift register
- To store
nbits, we requirenclocks. Each clock, 1 bit is shifted into the register. Do thatntimes to store the entire value you desire.- On the first rising edge, 0 may be loaded into the first flip flop. On the second rising edge, 0 is shifted into the second flip flop and, say, 1, is now loaded into the first.
- That repeats until every bit is loaded.
Load register
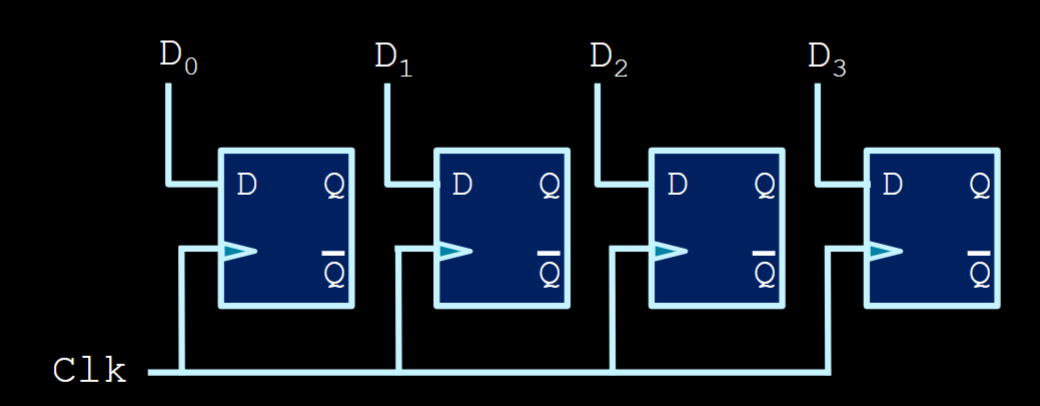
- You simply drive all
ninputs parallel into every flip flop of the register. - We can store the intended value in just 1 cycle.
- Right on the rising edge, the values will be stored!
Persistent data after storing what we want
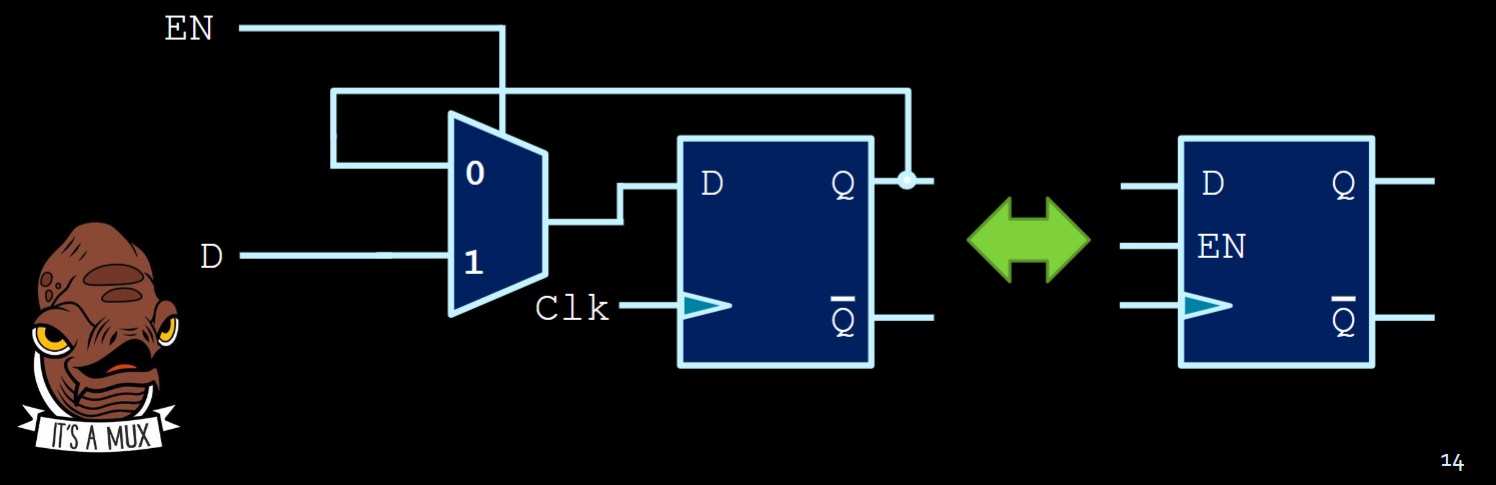
Sometimes we just want to keep the value and not change it every cycle. How to do that? Well with multiplexers!
- EN (enable) selects between the two modes (update; don’t update)
- When EN = 1, we load D (our input D goes into our load register)
- When EN = 0, the previous Q is fed back into the OG register (basically refreshing the first bit with the same value, thereby changing nothing)
- In the above, you can extend the register to be more than 1 bit by simply chaining the mux-d-flip-flop combo.
- Note that the MUX should always take from the
Qas that is what is stored. IfEN=0then we want to update the D-flip-flop with the old value so that nothing changes!- Observe the example below!
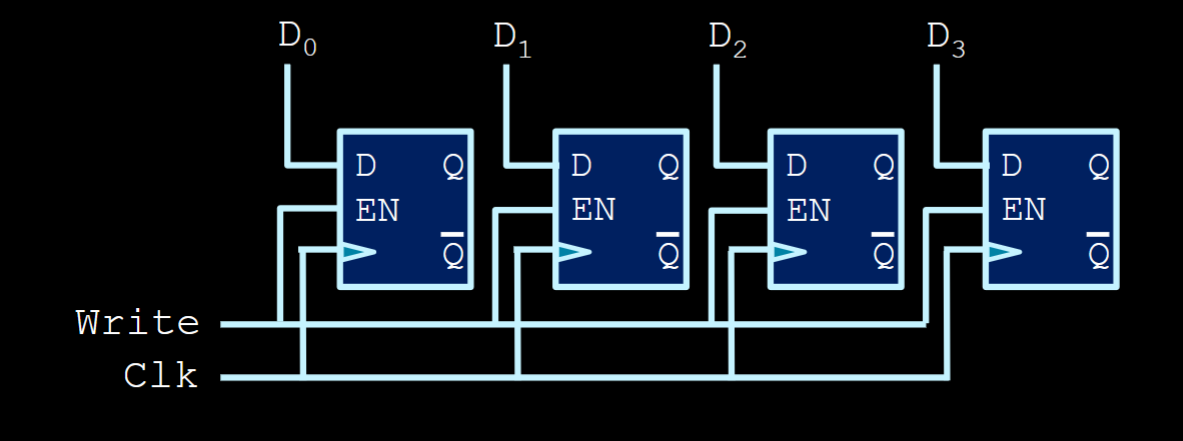
- Observe the example below!
- Boom, a complete load register!
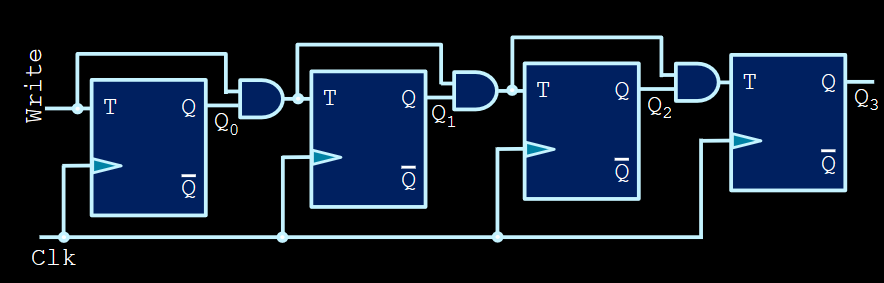 #todo i had notes on this but idk where it is lol
#todo i had notes on this but idk where it is lol
- If everything before is true, then flip the next guy. ye.
Shift Vs. Load
- Shift registers are serial (1 bit at a time)
- Load registers are parallel (loads bits all at once)
- This is bad cuz it creates complexity (and delay). It also uses more area.
- So usually serial is better.
Example: PCI uses parallel. PCIe is serial. However PCIe is faster! And yet less pins!!
